How to Use Microsoft Excel: 15 Essential Excel Formulas and Functions sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with casual formal language style and brimming with originality from the outset.
Readers will embark on a journey through the intricacies of Excel formulas and functions, gaining valuable insights into optimizing data analysis and manipulation.
Introduction to Microsoft Excel Formulas and Functions

Microsoft Excel formulas and functions play a crucial role in data analysis, helping users perform complex calculations, manipulate data, and automate tasks efficiently.
Formulas in Excel are used to perform calculations based on the values in designated cells, while functions are predefined formulas that simplify complex operations and provide specific results.
Common Scenarios for Excel Formulas and Functions
- Financial Analysis: Excel formulas are frequently used to calculate profits, losses, expenses, and other financial metrics.
- Data Visualization: Functions like SUM, AVERAGE, and COUNT help in summarizing and visualizing large datasets.
- Statistical Analysis: Excel functions like STDEV, CORREL, and TREND are essential for statistical calculations and forecasting.
- Conditional Formatting: Formulas are utilized to apply conditional formatting based on specific criteria, making data interpretation easier.
Basic Excel Formulas for Beginners
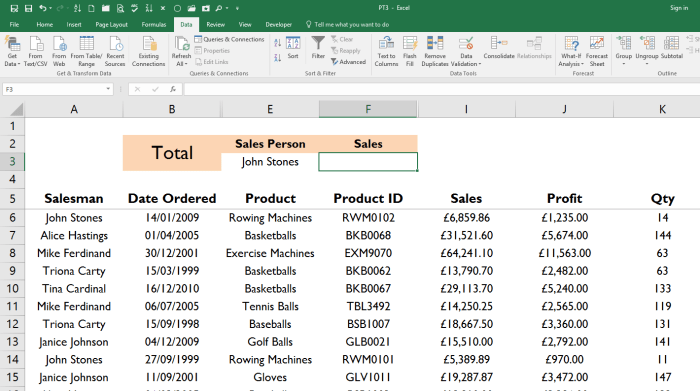
When starting out with Excel, it is essential to understand some basic formulas that are commonly used for calculations. These formulas can help you perform simple arithmetic operations and analyze data effectively.
Using SUM, AVERAGE, MIN, and MAX Functions
Excel provides built-in functions like SUM, AVERAGE, MIN, and MAX to quickly calculate totals, averages, and find the highest and lowest values in a dataset. These functions can save you time and effort when working with large sets of data.
- SUM Function: The SUM function is used to add up a range of numbers in Excel. For example, to find the total of cells A1 to A10, you would use the formula
=SUM(A1:A10)
.
- AVERAGE Function: The AVERAGE function calculates the average of a range of numbers. To find the average of cells B1 to B10, you would use
=AVERAGE(B1:B10)
.
- MIN Function: The MIN function returns the smallest number in a range. For instance, to find the lowest value in cells C1 to C10, you would enter
=MIN(C1:C10)
.
- MAX Function: The MAX function, on the other hand, gives you the largest number in a range. If you want to find the highest value in cells D1 to D10, you can use
=MAX(D1:D10)
.
By incorporating these functions into your Excel spreadsheets, you can streamline your calculations and obtain valuable insights from your data effortlessly.
Advanced Excel Functions for Data Analysis
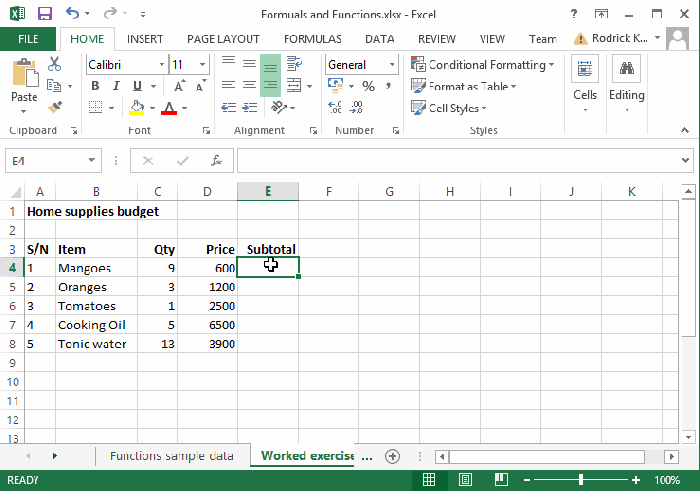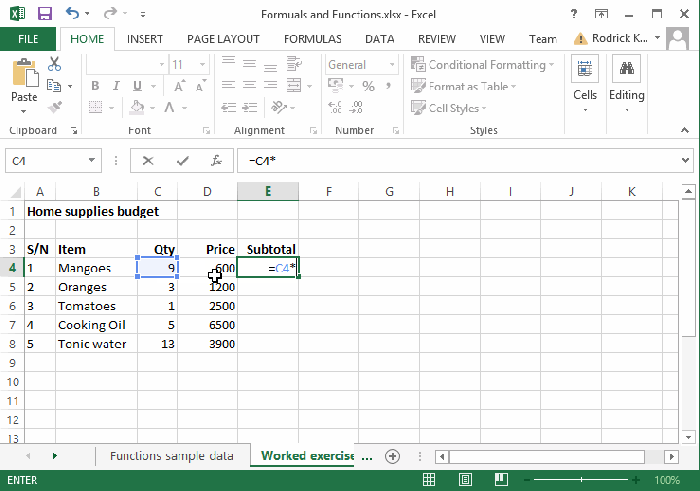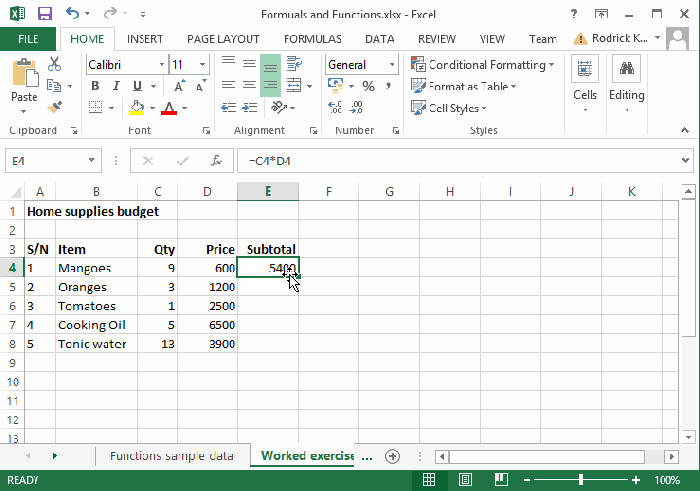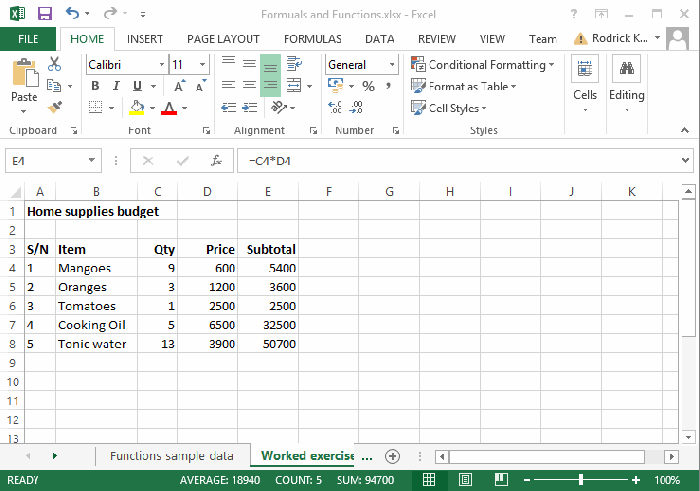
When it comes to analyzing large datasets in Excel, utilizing advanced functions can greatly enhance your efficiency and accuracy. In this section, we will explore key functions such as VLOOKUP, INDEX-MATCH, IF-ELSE, and CONCATENATE, highlighting their applications and benefits in data analysis.
VLOOKUP Function
The VLOOKUP function in Excel allows you to search for a value in the first column of a table and return a value in the same row from another column. This function is commonly used for tasks such as retrieving specific data points from a dataset or matching data from different sources.
- Ensure the data is sorted in ascending order for VLOOKUP to work correctly.
- Use absolute references for the table array to prevent errors when copying the formula.
- Consider using approximate match for numerical data and exact match for text data.
INDEX-MATCH Function
The INDEX-MATCH combination is a powerful alternative to VLOOKUP, offering more flexibility and accuracy in data retrieval. By using these two functions together, you can overcome the limitations of VLOOKUP, such as searching in any column and handling changes in the dataset more effectively.
- INDEX function returns the value at a specified row and column in a range.
- MATCH function locates the position of a value in a range.
- Combining INDEX and MATCH allows for dynamic data extraction and lookup.
IF-ELSE Function
The IF-ELSE function in Excel enables you to perform different actions based on a specified condition. This function is invaluable for data analysis tasks that require logical comparisons and decision-making processes.
- Structure the IF-ELSE formula with logical tests and corresponding actions for true and false outcomes.
- Use nested IF functions for multiple conditions and outcomes.
- Employ IF-ELSE to categorize data, calculate bonuses, or flag anomalies in datasets.
CONCATENATE Function
The CONCATENATE function in Excel allows you to join multiple text strings into a single string. This function is useful for combining data from different cells, creating customized labels, or formatting text in a specific way.
- Input text strings or cell references separated by commas within the CONCATENATE function.
- Consider using CONCATENATE with other functions like IF to generate dynamic text based on conditions.
- Concatenate can streamline data preparation tasks by merging information from various sources into a coherent format.
Final Summary

In conclusion, mastering these essential Excel formulas and functions opens up a world of possibilities for efficient data processing and analysis, empowering users to excel in their data-related tasks.