Embark on a journey of cultural adaptation with “How to Deal with Culture Shock: 7 Tips for Adjusting to a New Culture,” offering valuable insights and practical advice for navigating the challenges of adapting to a new environment.
Explore the stages of culture shock, coping strategies, and cultural adjustment techniques in this comprehensive guide.
Understanding Culture Shock
Culture shock is the feeling of disorientation or discomfort that someone may experience when they are exposed to a new culture or way of life. It can have a significant impact on individuals, affecting their emotional well-being, behavior, and overall adjustment to the new environment.
Common symptoms of culture shock include feelings of homesickness, frustration, anxiety, confusion, loneliness, and even physical symptoms like headaches or stomach aches. These symptoms can vary in intensity and duration depending on the individual and the extent of the cultural differences they are facing.
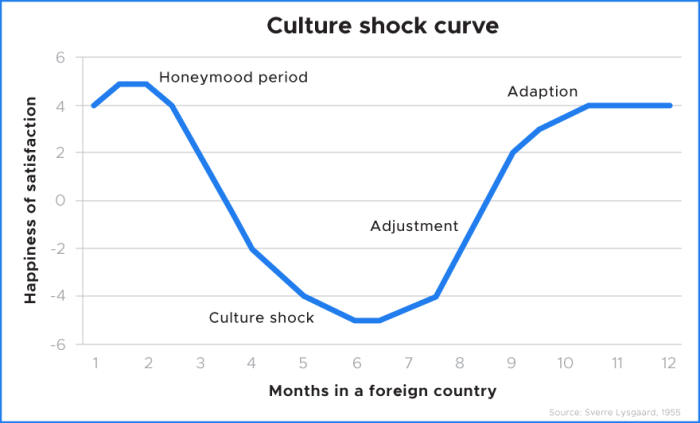
Stages of Culture Shock
The stages of culture shock are typically described as follows:
- Honeymoon Stage: This is the initial period when everything seems exciting and new. Individuals may feel enthusiastic and curious about the new culture.
- Distress Stage: As the novelty wears off, reality sets in, and individuals start to feel overwhelmed and frustrated by the cultural differences. Homesickness and feelings of isolation may intensify during this stage.
- Recovery Stage: In this stage, individuals start to adapt and find ways to cope with the challenges they are facing. They may seek out support, learn more about the culture, and develop strategies to navigate their new environment.
- Adaptation Stage: Finally, individuals reach a point where they feel more comfortable and integrated into the new culture. They have a better understanding of the customs, language, and social norms, which helps them feel more at ease in their new surroundings.
Coping Strategies for Culture Shock
Culture shock can be a challenging experience, but there are strategies that can help you navigate through it effectively. By staying open-minded, learning about the new culture, and connecting with locals, you can adapt and thrive in a new environment.
Staying Open-Minded
One of the most important coping strategies for culture shock is to stay open-minded. Embrace the differences you encounter in the new culture and try to see them as opportunities for growth and learning.
Learning About the New Culture
Take the time to educate yourself about the customs, traditions, and values of the new culture. This will not only help you understand the local way of life better but also show respect to the people in that culture.
Connecting with Locals
Building relationships with locals can provide you with a support system in the new culture. Reach out to people in the community, participate in local events, and engage in conversations to foster connections and feel more at home.
Cultural Adjustment Techniques

Adjusting to a new culture requires a combination of patience, open-mindedness, and willingness to learn. Cultural sensitivity plays a vital role in this process as it involves being aware and respectful of the values, beliefs, and customs of the new culture. By showing respect and curiosity towards the new culture, you can build positive relationships and navigate social interactions more effectively.
Role of Language Learning
Learning the language of the new culture is crucial in bridging cultural gaps. Language is not only a means of communication but also a reflection of the culture’s values and traditions. By learning the language, you can better understand the nuances of the culture, connect with locals on a deeper level, and participate more fully in daily life activities. Language learning can help break down barriers, foster relationships, and enhance your overall cultural experience.
Cultural Immersion Activities
Engaging in cultural immersion activities can help you adjust more effectively to a new culture. These activities involve actively participating in local customs, traditions, and events to gain a deeper understanding of the culture. Examples include attending cultural festivals, trying traditional foods, taking part in community celebrations, and joining local clubs or organizations. By immersing yourself in the culture, you can expand your knowledge, develop empathy, and form meaningful connections with the people around you.
Epilogue

In conclusion, mastering the art of adapting to a new culture is a gradual process that requires an open mind, willingness to learn, and a proactive approach to building connections. Use these tips to smoothen your transition and embrace the beauty of cultural diversity.