Starting with How to Prune Your Plants: 10 Pruning Techniques for Different Plant Types, this opening paragraph aims to draw in readers with an engaging overview of the topic, setting the stage for what’s to come.
Following this, detailed information about the topic will be provided in subsequent paragraphs.
General Pruning Techniques
Pruning is a vital practice in maintaining the health and promoting the growth of plants. It involves the selective removal of certain parts of a plant such as branches, buds, or roots to encourage proper development and improve overall appearance.
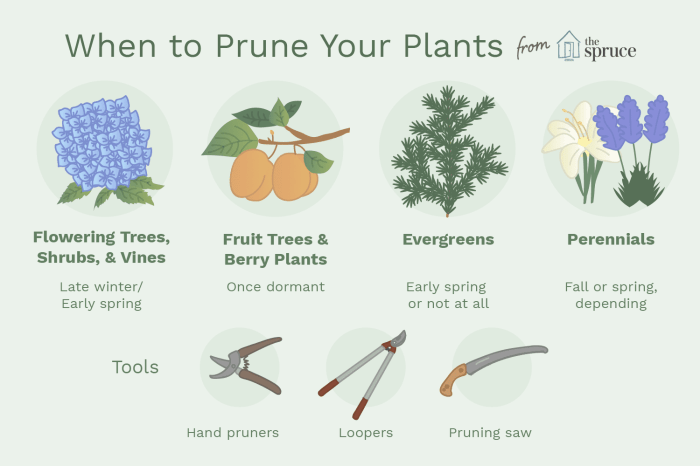
Identifying the right tools for pruning is essential to ensure the job is done effectively and safely. Some common tools used for pruning include pruning shears, loppers, pruning saws, and hedge trimmers. Each tool is designed for specific plant types and sizes, so it is crucial to use the appropriate tool for the job.
Shrubs, Trees, and Flowering Plants: Pruning Methods
- Shrubs: When pruning shrubs, it is important to focus on removing dead or diseased branches, as well as shaping the plant to maintain its desired form. Regular pruning can help promote new growth and flowering in shrubs.
- Trees: Pruning trees involves removing dead or damaged branches, thinning out dense areas to improve air circulation, and reducing the overall size of the tree if necessary. Proper pruning techniques can help trees stay healthy and prevent disease.
- Flowering Plants: Pruning flowering plants is essential for encouraging more blooms and maintaining a neat appearance. Deadheading, the removal of spent flowers, is a common pruning method for many flowering plants to stimulate new growth.
Best Time of Year for Pruning Different Plant Species
- Spring: Many plants benefit from pruning in early spring before new growth begins. This allows the plant to focus its energy on developing new shoots and flowers.
- Summer: Some plants, such as flowering shrubs, may require light pruning in summer to remove faded blooms and shape the plant for the rest of the season.
- Winter: Pruning in winter is ideal for deciduous trees and shrubs when they are dormant. It is easier to see the plant’s structure without leaves, making it easier to prune effectively.
Techniques for Pruning Fruit-Bearing Plants

Pruning fruit-bearing plants such as apple, peach, and citrus trees is essential for maintaining their health, promoting fruit production, and shaping their growth. Proper pruning techniques can help improve the quality and quantity of the fruit they bear.
Specific Pruning Needs of Fruit Trees
When it comes to fruit trees like apple, peach, and citrus, each type has specific pruning needs. Apple trees, for example, benefit from annual pruning to remove dead or diseased branches and promote air circulation. Peach trees require pruning to open up the canopy, allowing sunlight to reach the fruit and improve fruit quality. Citrus trees need selective pruning to remove crossing branches and maintain a balanced shape for optimal fruit production.
The Importance of Thinning Cuts in Fruit Tree Pruning
Thinning cuts are crucial in fruit tree pruning as they help reduce overcrowding within the tree canopy. By selectively removing branches, you can improve air circulation and light penetration, reducing the risk of disease and promoting even fruit ripening. Thinning cuts also help redirect the tree’s energy towards producing high-quality fruit.
Rejuvenating an Overgrown Fruit Tree Through Pruning
If you have an overgrown fruit tree, rejuvenating it through pruning can help restore its health and productivity. Start by removing any dead or damaged branches, followed by thinning out crowded areas to allow for better light and air circulation. Consider shaping the tree by cutting back long branches to encourage new growth and improve fruit production.
Impact of Pruning on Fruit Production and Tree Longevity
Pruning plays a significant role in fruit production and tree longevity. Regular pruning not only helps increase fruit yield by promoting healthy growth but also extends the lifespan of the tree by reducing the risk of disease and structural issues. Proper pruning practices can lead to healthier, more productive fruit trees that can provide bountiful harvests for years to come.
Techniques for Pruning Flowering Plants
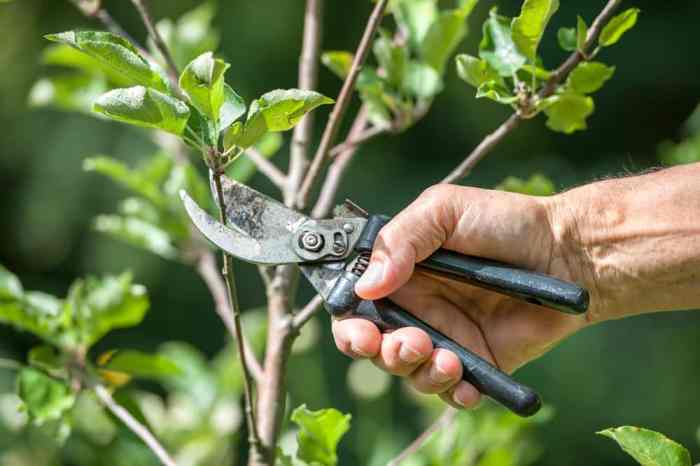

When it comes to pruning flowering plants, there are specific techniques that can help enhance their growth and blooming potential. Understanding the difference between deadheading and selective pruning is crucial for maintaining healthy and vibrant flowering plants.
Deadheading involves the removal of spent flowers to encourage new blooms and prevent the plant from putting energy into seed production. On the other hand, selective pruning focuses on removing specific branches or stems to shape the plant, improve air circulation, and stimulate growth.
Encouraging New Growth and More Blooms
- Regular deadheading of flowers that have faded or wilted can promote continuous blooming throughout the growing season.
- Selective pruning of older wood and crossing branches can help redirect the plant’s energy towards producing new growth and more flowers.
Shaping Flowering Shrubs like Roses and Hydrangeas
- For roses, prune in late winter or early spring to remove dead or weak branches and shape the plant for optimal growth.
- Hydrangeas benefit from light pruning after flowering to remove old blooms and encourage new growth. Avoid heavy pruning, as it can reduce flowering potential.
Hard Pruning vs. Light Pruning for Flowering Plants
- Examples of flowering plants that benefit from hard pruning include butterfly bushes and crape myrtles, which respond well to severe cutting back to promote new growth and blooming.
- Plants like lilacs and magnolias prefer light pruning to maintain their natural shape and encourage flowering without sacrificing too much growth.
Final Summary

Concluding with a captivating summary, this paragraph will wrap up the discussion on a high note, leaving readers with key takeaways.