Starting with How to Transplant Seedlings: 8 Tips for a Successful Transplant, the content unravels in an engaging and distinct manner, enticing readers into a narrative that ensures an informative and memorable experience.
The subsequent paragraph details the topic with clarity and precision.
Preparation for Transplanting Seedlings

When it comes to successfully transplanting seedlings, proper preparation is key to ensuring their survival and growth in a new environment. Here are some essential tips to consider before transplanting your seedlings:
Ideal Growing Conditions for Seedlings
Before transplanting your seedlings, make sure they have been grown in the ideal conditions to promote healthy growth. This includes providing them with sufficient sunlight, water, and nutrients. Seedlings should be well-established with strong stems and roots before being transplanted to prevent transplant shock.
Importance of Hardening off Seedlings
Hardening off seedlings is a crucial step in the transplanting process that helps acclimate them to outdoor conditions. This involves gradually exposing the seedlings to outdoor elements such as wind, sunlight, and temperature fluctuations. Hardening off seedlings reduces the risk of transplant shock and increases their chances of survival after being transplanted.
Tools and Materials Needed for Successful Seedling Transplant
To ensure a successful seedling transplant, you will need a few essential tools and materials. These include:
- Transplanting containers or pots
- Garden trowel or transplanting tool
- High-quality potting mix or soil
- Watering can or hose
- Labels for plant identification
- Protective gear such as gloves
Having the right tools and materials on hand will make the transplanting process smoother and more efficient, leading to healthier seedlings in their new environment.
Transplanting Techniques
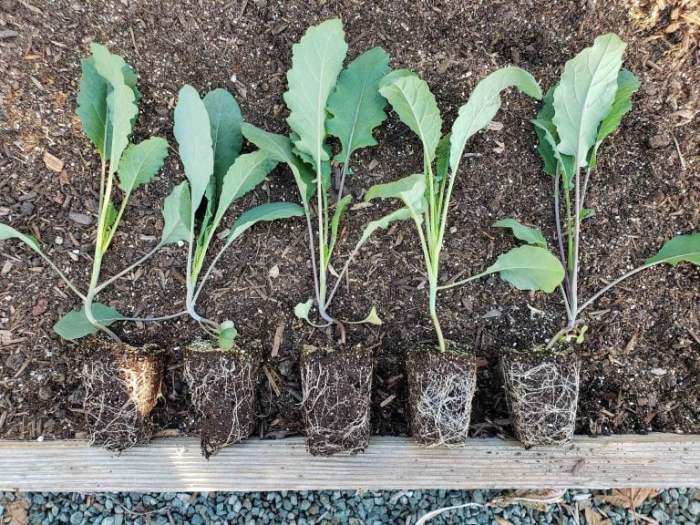

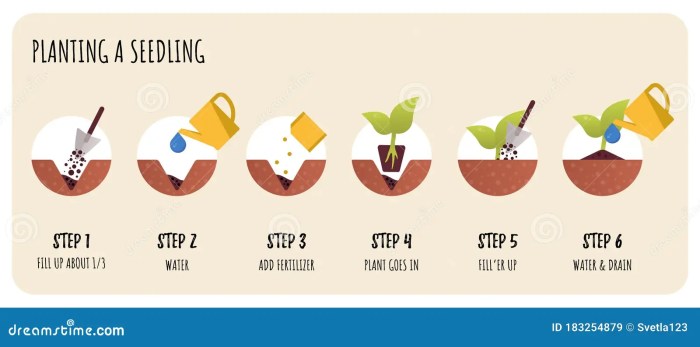
Transplanting seedlings is a crucial step in ensuring the successful growth of your plants. It involves carefully moving the young plants from their initial containers to a larger one or directly into the ground. Here, we will discuss the step-by-step process of transplanting seedlings, the correct depth and spacing for different types of seedlings, and common mistakes to avoid during the transplant process.
Step-by-Step Process of Transplanting Seedlings
- Water the seedlings thoroughly a day before transplanting to ensure they are well-hydrated.
- Prepare the soil in the new container or planting area by loosening it and adding compost for nutrients.
- Gently remove the seedlings from their original containers, being careful not to damage the roots.
- Dig a hole in the new soil that is slightly larger than the root ball of the seedling.
- Place the seedling in the hole and cover the roots with soil, pressing gently to secure it in place.
- Water the newly transplanted seedlings to help them settle into their new environment.
- Monitor the seedlings closely in the following days to ensure they are adjusting well to the transplant.
Correct Depth and Spacing for Transplanting Seedlings
- Transplant seedlings at the same depth as they were growing in their original containers to avoid burying the stem.
- Space seedlings according to their mature size to prevent overcrowding and competition for resources.
- For larger plants, such as tomatoes or peppers, space them at least 18-24 inches apart to allow for proper growth.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During the Transplant Process
- Avoid transplanting seedlings during the hottest part of the day to prevent transplant shock.
- Do not disturb the roots excessively when transplanting to minimize damage and stress to the plant.
- Avoid overwatering or underwatering the newly transplanted seedlings, as it can lead to root rot or dehydration.
- Make sure to harden off seedlings before transplanting them outdoors to acclimate them to the new environment.
Aftercare and Maintenance
After successfully transplanting seedlings, it is crucial to provide proper aftercare and maintenance to ensure their healthy growth and development. This includes watering, protecting from pests and diseases, and adjusting light exposure as needed.
Watering Newly Transplanted Seedlings
Watering is essential for the survival of newly transplanted seedlings. Here are some tips to ensure proper watering:
- Water the seedlings immediately after transplanting to help them settle into their new environment.
- Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to root rot. Allow the top inch of the soil to dry out slightly before watering again.
- Water the seedlings at the base to prevent water from splashing onto the leaves, which can cause fungal diseases.
- Monitor the moisture levels regularly and adjust watering frequency based on the needs of the seedlings.
Protecting Seedlings from Pests and Diseases
After transplanting, seedlings are vulnerable to pests and diseases. Here’s how you can protect them:
- Inspect the seedlings regularly for any signs of pest infestation or disease. Remove affected leaves or plants immediately to prevent the spread.
- Use organic pest control methods such as neem oil or insecticidal soap to treat common pests like aphids or spider mites.
- Practice crop rotation and maintain good garden hygiene to prevent the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil.
Adjusting Light Exposure for Transplanted Seedlings
Proper light exposure is crucial for the growth of seedlings post-transplant. Here are some tips to adjust light exposure:
- Gradually introduce the seedlings to direct sunlight if they were previously grown indoors or in a shaded area. Start with a few hours of sunlight per day and increase gradually.
- Monitor the seedlings for any signs of sunburn, such as wilting or yellowing leaves. Provide shade during the hottest part of the day if needed.
- Ensure that the seedlings receive adequate light for photosynthesis to promote healthy growth and development.
Concluding Remarks

Concluding with a captivating summary, the closing paragraph leaves a lasting impression and wraps up the discussion effectively.